On Soft Skills: Effective Communication
Your audience, medium, and delivery will determine how effectively you communicate with others.
Communication is the process of interpreting & conveying a message. It is a vital soft skill that plays a crucial role in all aspects of our personal and professional lives.
Introduction to Effective Communication
Effective communication is more than just exchanging information; it is about understanding the intent behind the message and ensuring clarity in your interactions. In the workplace, this skill is a foundational element for professional success. When team members communicate openly and clearly, it fosters an environment of collaboration and trust, which can significantly enhance productivity and innovation. Moreover, effective communication allows for constructive feedback and problem-solving, enabling teams to navigate challenges more efficiently.
Why is Communication Important?
Effective communication allows us to clearly express our thoughts, feelings, and ideas to others. It also helps us understand the perspectives of others and avoid misunderstandings or conflicts. In the workplace, good communication leads to efficient teamwork, better decision-making processes, and improved productivity. It also promotes a positive work culture and builds strong relationships among team members. This is due to:
Transparency: when team members share information openly, it bridges gaps in understanding and encourages a culture of trust. This trust empowers individuals to express their ideas without fear of judgment, leading to creative solutions and collaborative efforts.
Conflict Resolution: by actively listening to differing viewpoints and articulating one's own perspective with clarity, misunderstandings can be mitigated before they escalate into larger issues. Communication is a two-way street: it requires both expressing ourselves and being receptive to others. This balance nurtures a supportive environment where diverse opinions are valued, enhancing team dynamics.
Professional Development: individuals who can convey their thoughts clearly and persuasively are often viewed as influencers, regardless of their official title. This ability opens doors to opportunities for advancement, allowing one to influence and inspire others.
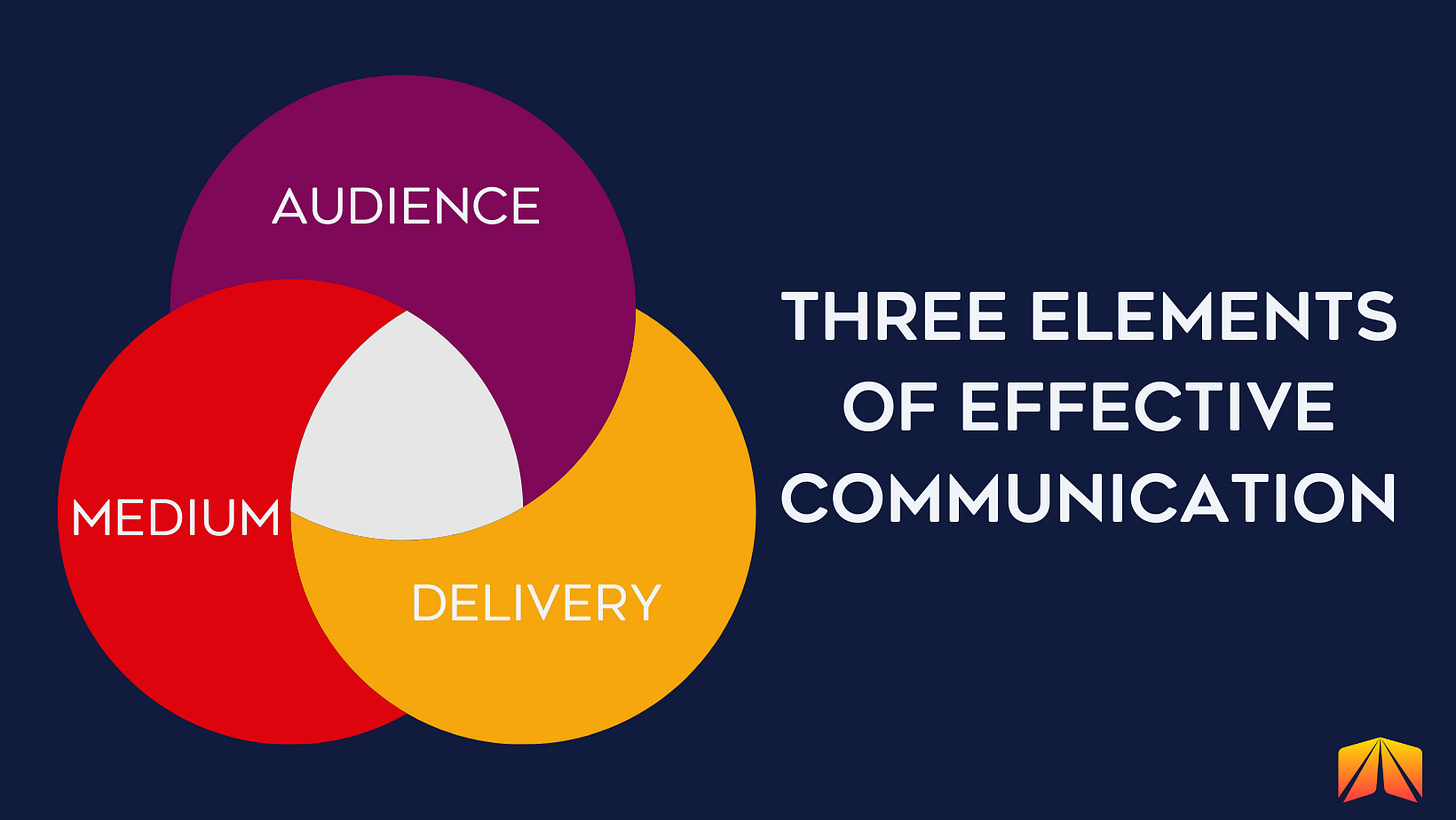
Three Elements of Effective Communications
To be an expert communicator, it is essential to understand its three core components: audience, medium, and delivery.
Audience: Who the Message is For
Understanding your audience is crucial; it involves recognizing their needs, expectations, and preferred communication styles. Tailoring your message to resonate with your audience not only enhances comprehension but also fosters a connection.
Whether you’re delivering a presentation, sending an email, or engaging in casual conversation, being aware of who you are addressing allows you to tailor your message appropriately. This introspective approach enhances the clarity of your communication and increases its impact.
Considering Your Audience
When tailoring your message to your audience, consider three factors: their background, expectations, and knowledge level
For instance, when speaking to a group of experts in a specific field, you may choose to use technical jargon and delve into complex concepts, knowing they possess a foundational understanding.
Conversely, when communicating with individuals who may be less familiar with the topic, simplifying your language and focusing on the key points will ensure your message is accessible. This adjustment fosters a supportive atmosphere that encourages engagement, keeping your audience attentive and open to your ideas.
Being mindful of your audience's potential concerns and motivations allows for a more empathetic interaction. It enables you to address their needs and questions proactively, which builds trust and strengthens relationships.
Ultimately, effective communication is less about delivering information and more about creating a meaningful exchange that values the perspectives of all participants involved.
Medium: The Form of Communication
The medium refers to the method or channel through which the message is conveyed. Choosing the right medium can significantly impact how the message is received. For instance, sensitive topics are often best discussed face-to-face to ensure empathy and immediate feedback.
There are three types of communication mediums, each with a variety of channels:
Verbal Communication: this involves using spoken words or sounds to convey a message, such as face-to-face conversations, presentations, emails, or phone calls. Verbal communication is the most common form of communication and can be either formal or informal.
Non-Verbal Communication: this includes body language, facial expressions, gestures, eye contact, and tone of voice. Non-verbal cues can often convey more meaning than words and are essential in understanding the underlying emotions or motivations behind a message.
Written Communication: Any form of written information exchanged between individuals falls under this type of communication. Written communication can be formal or informal, depending on the audience and expectation for communication.
Choosing the Appropriate Medium for Communication
Selecting the appropriate medium and channel for your communication is essential to ensuring that your message is not only understood but also received in the spirit intended. Here’s how to navigate this decision-making process thoughtfully and effectively:
Assess the Nature of the Message: Begin by evaluating the content and context of your message. Is it sensitive, complex, or requires immediate feedback? For example, challenging conversations or discussions that involve emotional content are often best handled face-to-face. This allows for nuanced dialogue and the opportunity to read non-verbal cues that can aid understanding.
Know Your Audience: Consider audience preferences, communication styles, and the relationship you share. If your audience feels more comfortable with written communication, such as emails or reports, catering to that can foster openness and engagement. Conversely, for discussions that require brainstorming or collaborative problem-solving, face-to-face meetings or group discussions might be more effective.
Evaluate the Urgency and Timing: The urgency of the message also plays a vital role in your choice of medium. If you need to communicate something quickly or require immediate responses, telephonic conversations or instant messaging platforms can facilitate prompt interaction. If the message is less urgent, an email or a report might be appropriate, giving the recipient time to reflect on the information.
Consider the Complexity: If your message is multifaceted and requires detailed explanations or visuals, opt for a presentation format or a detailed written document that allows room for elaboration. For straightforward updates or announcements, a brief email or even a shared document can suffice.
Feedback and Interaction Needs: Finally, reflect on how crucial it is to gather feedback. Mediums that allow for real-time interaction, such as video calls or face-to-face meetings, encourage an immediate exchange of ideas and opinions. In contrast, written communication may necessitate follow-ups for clarification, which can slow down the dialogue process.
By considering these factors, you can make informed decisions about which medium and channel will effectively convey your message.
Delivery: How a Message is Interpreted
Delivery encompasses the manner in which you present your message. This includes tone of voice, body language, and pacing. Up to 93% of communication is how a message is conveyed with body language, tone and inflection. An engaging and confident delivery can captivate your audience, while a distracted or negative tone can cloud even the clearest message.
Here are some tips for improving your delivery and ensuring your message is interpreted correctly:
Maintain a Positive Attitude: Your attitude can greatly impact how your message is received. Approach the conversation with positivity, openness, and confidence to create a welcoming environment for communication.
Be Mindful of Non-Verbal Cues: As mentioned earlier, non-verbal cues play a significant role in communication. Pay attention to your body language, gestures, and facial expressions to ensure they align with your intended message.
Use Appropriate Tone and Inflection: The tone of voice you use when delivering a message can convey different emotions and attitudes. Be aware of how you sound to others.
Together, these components create a holistic approach to effective communication, ensuring clarity, fostering connection, and amplifying the impact of your message.
Building Strong Communication Skills
Like any other skill, effective communication can be learned and improved upon. Here are some tips for building strong communication skills:
Listening: pay attention to what others are communicating to you without interrupting or judging. Active listening is a crucial component of effective communication.
Clarity: be concise and to the point, using simple language that is easily understood.
Confidence: pay attention to your body language, tone of voice, and facial expressions as they can convey more meaning than words alone.
Empathy: try to understand the perspective of the other person and consider their feelings when delivering your message.
Developing strong communication skills requires practice and reflection. Here are some exercises you can incorporate into your routine to enhance your abilities:
Active Listening Role-Play: Partner with a colleague or friend and engage in a dialogue where one person shares a personal experience while the other practices active listening. Afterward, the listener should summarize what was said, including emotions and key points. This exercise helps improve concentration and reinforces the importance of understanding the speaker's perspective.
Feedback Sessions: Organize regular feedback sessions with peers where you can share ideas or present topics. Encourage constructive criticism on your communication style, clarity, and delivery. This creates an environment of open dialogue and allows for continuous improvement.
Tone Variation Practice: Choose a script or paragraph and read it aloud multiple times, altering your tone and pacing with each delivery. Experiment with expressing different emotions, such as enthusiasm, sadness, or anger. This exercise helps you become more aware of how tone influences the message and can enhance your delivery skills.
Non-Verbal Awareness Exercise: Spend a day consciously paying attention to your own body language and the non-verbal cues of others. Reflect on instances where your body language complemented or contradicted your verbal messages. At the end of the day, write down your observations and identify areas for improvement.
Concise Communication Challenge: Challenge yourself to summarize a complex topic in just a few sentences while maintaining key details. This exercise fosters clarity and helps you practice being succinct, a vital element for effective communication.
By incorporating these exercises into your personal and professional development, you will build strong communication skills to serve you well across your career.